What is a Non-Ribosomal Peptide?
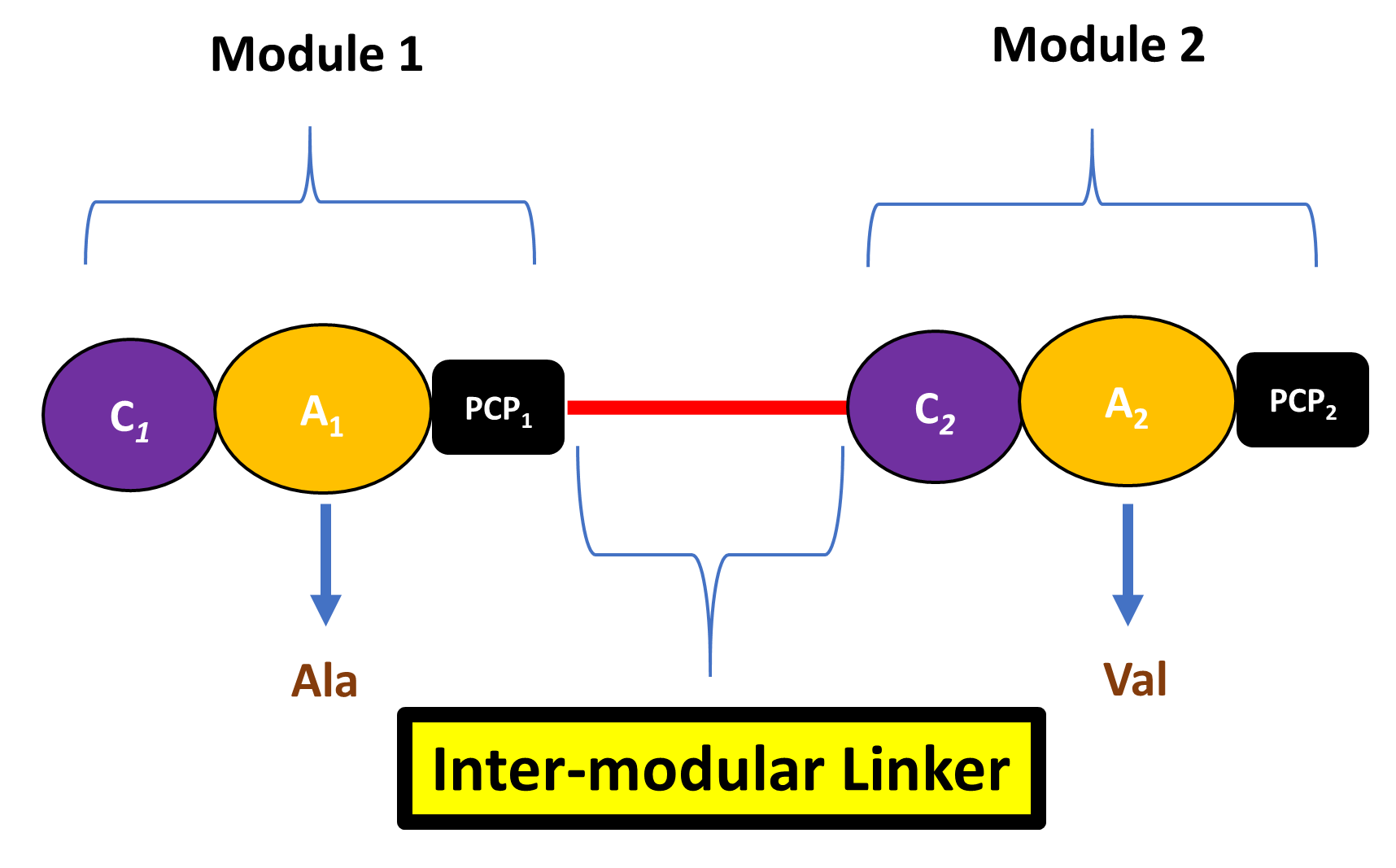
Non-ribosomal peptides(NRPs) are secondary metabolites produced by bacteria and fungi that could find many clinical applications, mainly antibiotics (e.g. Daptomycin, Vancomycin), but also anticancer (e.g. Bleomycin), and immunosuppressants (e.g. Ciclosporin). NRPs are synthesized by a cluster of enzymes known as non-ribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPSs). NRPSs are exceptional mega-enzymes, with multi-modular catalysts that work together to assemble highly complex, bioactive secondary metabolites of peptide origin (Elizabeth A Felnage et.al). Each NRPS subunit is composed of modules. Each module incorporates one monomer into the NRP product. Each module can be subdivided into catalytic domains. The four catalytic domains that are found on most NRPSs are Adenylation (A) domain, Thiolation or peptidyl carrier protein (PCP) domain, Condensation (C) domain, Thioesterase (TE) domain. The A domain is responsible for selecting the substrate and activating it, a small peptidyl carrier protein (PCP) domain carries the activated amino acid and propagates the growing peptide chain, and a condensation (C) domain links amino acids of two adjacent modules via a condensation reaction. An example of a NRP: Tyrocidine Biosynthetic gene cluster (Mootz HD et.al).(fig.1).

What is an Inter-Modular Linker?
An IML is the segment of amino acids linking two successive NRPSs modules. It could come between a C-domain of module 1 and PCP-domain of module 2 (most of the cases). However, it could also show up between a tailoring-domain of module 1 and PCP-domain of module 2. Tailoring domains are special domains that are responsible for modifying the amino acid substrate before it is incorporated into the peptide chain (e.g. epimerization domain (E) which catalyzes the L to D amino acid conversion).
Importance of NRP Inter-Modular Linkers Database
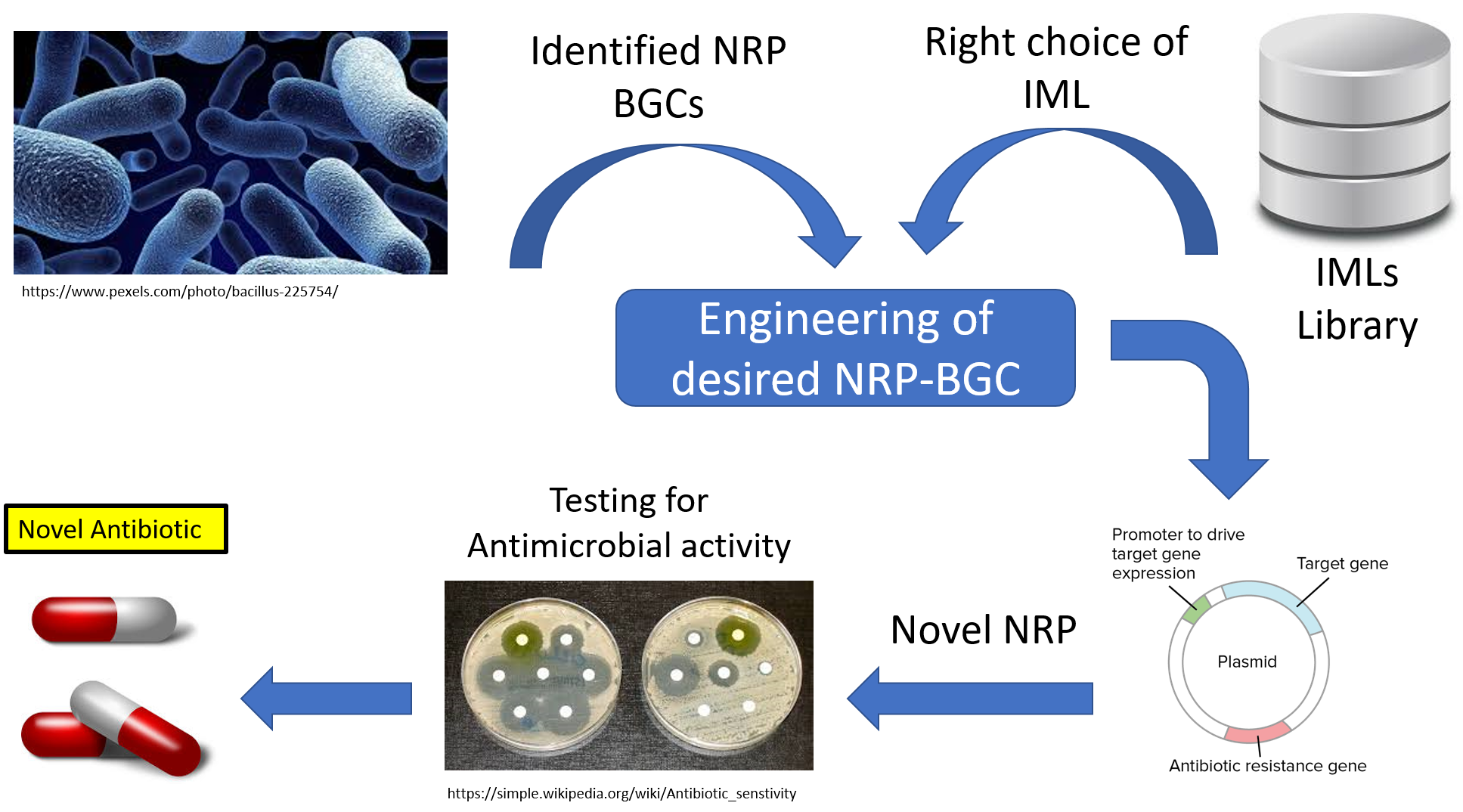
Creating the first computational tool dedicated for extracting and analyzing of IMLs within NRPSs and establishing the first IMLs database, will be a big asset for researchers interested in combinatorial biosynthesis and rational design of novel NRPs. Following the outcome of our tool with a rigorous experimental validation, will certainly open the door for successful molecular engineering strategy of NRPs, that will lead not only for the synthesis of peptides with potential anti- microbial activity but also others with a wide range of activities such as anticancer, immunosuppressant, antiviral and antifungals.