* Our tool processes non-ribosomal peptide biosynthetic gene clusters after being identified using the AntiSMASH tool.
In the process of scanning and identifying NRP BGCs, AntiSMASH uses three algorithms to predict the specificity of the NRPS adenylation domain
(Minowa .et.al, Roettig, M et.al,
Stachelhaus et.al). If all three algorithms agree on the same predicted substrate then it will be used as the substrate of choice by AntiSMASH,
otherwise, AntiSMASH uses the term 'nrp' for all unidentified NRPS substrates. Hence, some IMLs may look as follows (e.g Ala-linker-Ser), if both substrates are well identified, others will look like (nrp-linker-Ser)
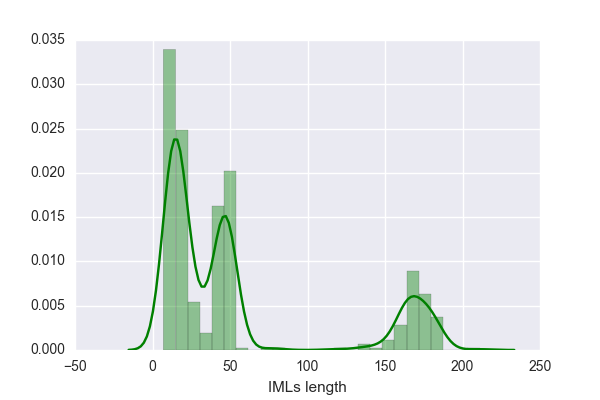
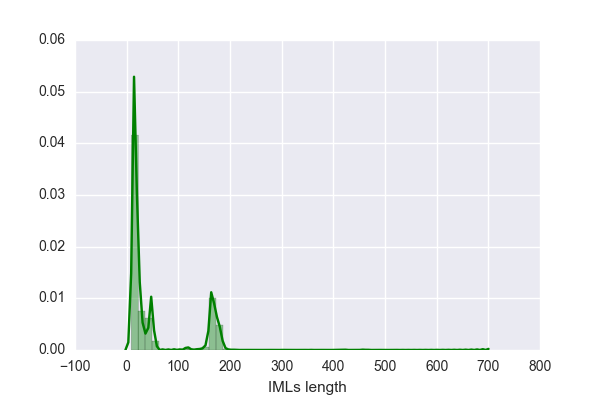
or even sometimes (nrp-linker-nrp), with one or two unidentified substrates. Thus under each Data (MIBiG and NCBI), there are two tables, one where all linkers are included (larger data) and the other one lacks all "nrp containing linkers" (smaller data).